19
2023
-
05
Introduction to Cindless Mill Dressing Skills
Source:
When I first came into contact with centerless grinding, I did not understand some basic concepts such as center height, diamond trimming pen offset, trimming angle, inclined angle guide wheel trimming, etc. Although I could complete simple grinding operations according to the steps instructed by the master, I only knew it and did not know why. Cindless grinding is a very practical technology, even if the same equipment with the same setting conditions novice and experienced master grinding out the effect may also have a big gap. To put it bluntly, after a certain degree of experience and the feeling of hands far exceed the tens of thousands of words of operating instructions. This is also why sometimes the old masters of debugging and installation of careless grinding manufacturers may not know much about the contents of their company's operating instructions. Because most of the operating instructions are printed out by the designers of the technical department in front of the computer, there is nothing they can do about the unspeakable [feeling]... It is of course very important for beginners to have good or bad understanding of books, but after I understand the basic concepts, I will get twice the result with half the effort for further improvement. The experts will not have to waste precious time to look down. Beginners should be the reference. After such a long period of nonsense, the following will get down to business.
There is nothing to say about the trimming of the guide wheel when cutting into the grinding. The trimming angle and inclination angle are both zero, and the guide wheel is cylindrical after trimming. At this time, it does not matter the offset of the diamond pen.
When grinding, the force to move the workpiece forward is needed to make the workpiece rotate and advance. Obviously, there is no way to apply forward thrust to the workpiece if the workpiece is parallel to the guide wheel shaft like cutting into the grinding. Then for the workpiece on the pallet, considering the supporting force of the grinding wheel, the guide wheel and the pallet, if you want to generate a force to push the workpiece forward, you can only make a fuss on the guide wheel. Naturally, the following basic concepts are involved. Heart height, diamond pen offset, tilt angle, dressing angle, guide wheel speed, workpiece moving speed and other issues. For convenience, itemize common basic problems.
In addition, find out what shape the so-called single-page hyperboloid is. Imagine a cylindrical shape as two equal-diameter circles connected together by equal long line segments. The upper and lower circles rotate in opposite directions around the central axis. At this time, the equal-length line segments will form a single-page hyperboloid shape with thin middle and thick ends. If conditions permit, you can directly take a cylindrical cage and twist it by hand, which is more intuitive.
1) Why set the standard of heart height and heart height?
This problem involves the rounding principle of centerless grinding. If you are interested, you can search the Internet or find a book to study it, and you can basically understand it. The simple way to consider is to consider what will happen if there is no heart height, that is, the center of the workpiece and the center of the guide wheel are equidistant, and the top surface of the pallet is horizontal? At this time, when the workpiece rotates, the protruding part contacts the guide wheel surface, and the protruding part contacts the grinding wheel opposite to the part, which will be ground down a little bit. If the workpiece is ground repeatedly, the final result will be ground into an equal diameter prism circle. (In the actual production process, the principle of rounding is relatively common. Similar) If the center height is higher than the center of the guide wheel and the grinding wheel, the convex and concave parts of the workpiece will not be on the same diameter, the convex will be continuously worn away, and the concave part will be continuously shallower.
The setting range of heart height can be calculated according to the following formula: H = 0.04(Dr Dw) H heart height Dr guide wheel diameter Dw workpiece diameter (this is an approximate value, which will be increased or decreased according to the grinding effect after initial setting)
2) Why set the offset and the calculation method of the offset?
In order to ensure the stability of the workpiece in the grinding process, the top of the pallet is designed as an inclined surface, and the workpiece is inclined in the direction of the guide wheel, similar to the V-groove support. The existence of the inclination angle of the guide wheel gives the workpiece a source of force for forward movement. But just by tilting the guide wheel, there will be new problems. Imagine the contact between the workpiece and the guide wheel in the state of cutting into the grinding. In fact, a straight line on the guide wheel surface contacts with a straight line on the workpiece surface. What happens when one of the two straight lines tilts? Only the middle point intersects, right? Naturally, there is no grinding. The workpiece and the guide wheel are in point contact rather than line contact.
How to avoid this situation? Change the shape of the guide wheel. The guide wheel can still be in line contact with the workpiece on the pallet after tilting. Obviously, the two heads of the middle of the thick drum, and cylindrical are not enough to meet the needs. So what if the guide wheel is a shape with a thin middle and two thick ends? This is the knowledge of the single-page hyperboloid mentioned earlier. A straight line on the surface of a single-page hyperboloid is an oblique straight line.
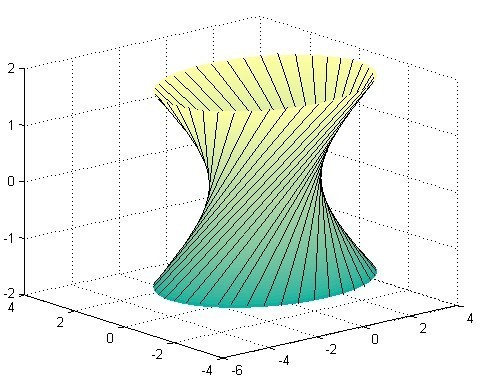
Obviously, as long as the inclination angle of the inclination angle of the guide wheel can be close to the angle of the straight line of the curved surface, the contact between the guide wheel surface and the workpiece can be ensured to be in a line contact state.
So how can I trim the guide wheel into the shape above? The grinding wheel dresser swings at a certain angle!
For ease of understanding, let's first explain the case where only the finisher is swung and the diamond pen offset is zero. The moving trajectory of the diamond pen is a straight line.
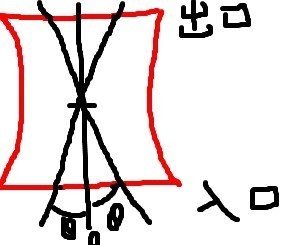
After the trimming angle swings, the diamond pen track and the contact line of the guide wheel surface intersect at a point in the center of the guide wheel surface, that is, when trimming the guide wheel, the diamond pen and the middle of the guide wheel surface contact first, and the middle part will sag down after trimming back and forth, presenting a hyperboloid with the same diameter at both ends. As shown in the above figure, the shape of the same angle guide wheel swinging left and right is also the same.
After the diamond pen is offset, the shape is as shown in the following figure.

The black line is the diamond pen trimming track. The shape of the guide wheel obtained when the dresser is swung left and right.
After the diamond pen is offset, the front end or the rear end of the trimmed guide wheel shape is large according to whether the trimming angle is left or right. The reason is that there is a difference between the distance between the diamond pen and the guide wheel surface after the diamond pen is offset.
The simplest way is to take a web as a guide wheel and a pen as a diamond pen to simulate the offset.
The offset of the diamond pen is about 90% of the heart height. The offset is Ht = 0.9H.
3) Why is the tilt angle set? The relationship between the tilt angle and the speed of the guide wheel and the moving speed of the workpiece?
Write here to find this problem has been discussed before. Since it is a pre-written outline, let's just write it down like this.
The greater the angle of inclination, the greater the forward force on the workpiece and the faster the corresponding workpiece movement. In detail, the words involve trigonometric functions. When I was in school, I hated trigonometric functions and stopped talking about them. It may be better to imagine the extreme situation. When the inclination angle is zero, the forward force of the workpiece to the workpiece is zero, and the inclination angle is assumed to be perpendicular to the workpiece. The workpiece and the guide wheel surface contact at the middle point, and the force to the workpiece is the largest. Then the inclination angle slowly increases from zero, and the thrust of the workpiece gradually increases.
By the way, the moving speed of the workpiece is the production efficiency of the heartless mill. The inclination angle of the guide wheel and the speed of the guide wheel can be obtained according to a certain combination, and different moving speeds of the workpiece can be obtained. Generally, it can be found in the equipment instruction manual.
That is to say, according to the requirements of production efficiency, the tilt angle and the speed of the guide wheel are set. In the combination of choice to avoid the grinding wheel inclination and speed limit. (For example, if the guide wheel speed is 200-300rpm/or the inclination angle is 4-5 degrees)
4) What is the difference between the left and right swing of the trimming angle? What is the relationship between the trimming angle and the tilt angle?
The influence of the trimming angle swinging left and right on the shape of the guide wheel after trimming can be referred to the above content. Under normal circumstances, when grinding bars and slender shafts, the dresser swings to the left, and the front end of the guide wheel is large and the rear end is small. When grinding, the workpiece enters the front grinding area for spark grinding, the rear end is cleaned, and then it can be smoothly exported from the outlet.
The dresser has a right swing and a large rear end of the guide wheel, which is mainly used for grinding workpieces like bearing sleeves. When such workpieces are ground at the bottom of the height, the stability is poor. After the grinding of the front end of the large workpiece at the rear end of the guide wheel is completed, the moving speed into the grinding area is reduced, and the workpiece at the rear supports the workpiece at the front.
The relationship between the trimming angle and the inclination angle: the trimming angle is about 90% of the inclination angle θt = θX 0.9
5) Why should the trimming angle be smaller than the inclination angle?
First consider the case of zero inclination angle, the contact point between the trimmed guide wheel and the workpiece is at two points at the entrance and exit.

If the inclination angle is exactly equal to the trimming angle of the guide wheel, the straight line on the surface of the guide wheel and the straight line of the workpiece contact surface coincide completely. This situation returns to the same situation as in the cut-in mill. The workpiece has no forward thrust and cannot move forward, so grinding cannot be carried out. (My understanding here may be biased, and I hope the expert can give me some advice.)
If the inclination angle is greater than the trimming angle, the relationship between the guide wheel surface and the workpiece is as follows

It may be difficult to understand why the shape of the guide wheel becomes convex. This is a view looking down from directly above the guide wheel. It can also be understood as a shape after making a cut perpendicular to the pallet along a straight line at the top of the pallet.
Take a paper tube and press it down with your hand to form a thin shape in the middle. Replace the workpiece with a pen. When the inclination angle increases, see if the distance between the two ends and the pen has increased. If this part cannot be understood, it will be more difficult to understand when it comes to the concept of grinding area in the future.
To sum up, the center height is calculated according to the size of the actual workpiece, and the offset is found according to the efficiency requirements of the actual production to find the corresponding guide wheel speed and inclination angle, and the trimming angle is calculated from the inclination angle. Commonly used formulas are used for reference.
H = 0.04(Dr Dw) Ht = 0.9H H Heart Height Ht Diamond Pen Offset
Θ t = Θ x 0.9 Θ tilt angle Θ t trim angle
The above is only an approximate value and can only be used as an initial setting reference value, which should be adjusted according to the needs of the workpiece and actual production.
At this point, I have also roughly finished some basic concepts. I thought it was easy to speak clearly, but when I wrote it, I felt that my words did not reach my meaning. I'm not an expert at most just a beginner wandering around the door of unwickedness grinding. Think of it as your own learning summary. It's a joke. If any senior expert patiently endures a smile to see here, also expect to be able to give some advice to be very grateful.
Articles are reprinted works.
Previous Page
Related Articles
Sweep the mobile phone browsing

Contact Us
International sales manager: John Mob: +8618539115199
Email: xydgbcn@gmail.com
Add: Gutuo Village, Chengliu Town, Jiyuan City, Henan Province
©2022 Jiyuan Xinyang Metal Chrome Rod Co., Ltd. Copyright All Rights Reserved Website Supports IPV6
